Genetic studies
At Advanced Fertility Center Cancún, we offer the most advanced and safest options to protect your reproductive health and increase your chances of achieving a successful pregnancy. Through our genetic testing and gender selection services, we provide the tools to make informed decisions, always with an ethical and personalized approach—helping ensure the birth of healthy babies.
We also offer genetic testing before, during, and after pregnancy, supporting you through every stage of your journey.
One of our specialists will guide you in determining which tests are right for you, based on your medical history, reproductive goals, and current clinical recommendations.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
PGT-A
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidies (PGT-A)


It is an embryonic genetic analysis for the detection of abnormalities in the number of chromosomes (medically known as aneuploidies), which means that there is a greater or lesser number of one or more chromosomes in the embryo.


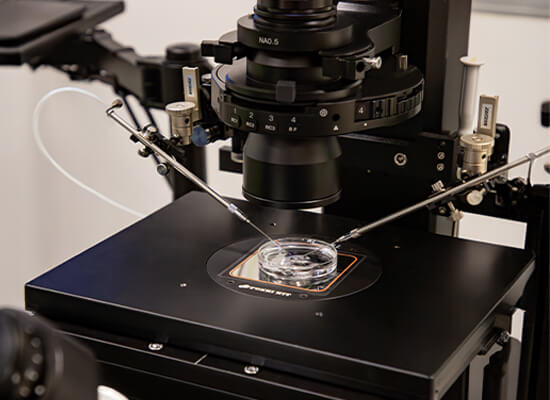
On day 5 of embryo development, we perform a biopsy in the laboratory, known as a trophectoderm biopsy.
This embryo fragment (biopsy) is sent to a genetics laboratory for amplification and analysis, where we receive the results within 2-3 weeks.
Contact our specialists if you are looking to have a boy or a girl.
Most relevant benefits of PGT-A
- It allows the selection of genetically normal embryos with a higher probability of success.
- Reduces the risk of miscarriage
- Increase implantation and pregnancy rates


Preimplantation screening for mutations (PGT-M)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic Conditions (PGT-M)
It is a study that allows us to find an altered gene (specific mutation) in embryos. It is generally used for people who are known carriers of an altered gene, mutation, or a dominant genetic disease. These detections can be performed with a Carrier Panel or by specifically searching for a mutation that runs in their family.


Contact our specialists for guidance on the types of genetic diseases they can detect.
Preimplantation for structural translocations (PGT-SR)
Preimplantation genetic screening for structural translocations (PGT-SR)
A translocation is a structural arrangement of genes, different from normal, where a chromosome fragment from one pair is exchanged with a chromosome fragment from another pair – usually detected by karyotyping – and can be of two types:
Balanced Translocation
Both fragments are the same size and molecular weight, so they generally do not cause problems in the phenotype (the way genes are expressed), but they can be inherited and expressed differently in offspring.
Unbalanced Translocation
In this case, the fragments gained or lost through translocation impact the phenotype (genetic expression) of the person, so there will be genetic diseases that are expressed at different levels.

Carrier Screening Panel
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, half inherited from each parent. Most of us carry minor gene mutations — usually harmless unless both copies of a gene are affected.
A carrier screening panel helps identify these mutations and compares them between partners or donors to assess the risk of passing on genetic conditions to a baby.
If both partners carry the same mutation, PGT-M can be performed to screen embryos for that condition.


In cases where both partners are found to be carriers of the same altered gene (mutation), a preimplantation genetic screening for mutations (PGT-M) can be performed to detect the disease in embryos.
This test allows us to analyze genes to detect common mutations in humans. There are a wide variety of carrier panels, ranging from a few genes, panels for specific risk populations, and mitochondrial inheritance panels, to a complete exome scan/analysis of all genes in a human being, known by its name in English as a Whole Exome Panel.
Some examples of diseases it can detect are blood disorders such as thalassemias or hereditary anemias, cystic fibrosis, hemochromatosis, retinitis pigmentosa, fragile X syndrome, among others. Thus, it is capable of detecting diseases with different types of inheritance:
- Dominant
- Recessive
- X-linked
- Linked to the Y chromosome
- Mitochondrial
Karyotype
A karyotype is the genetic makeup of a human being. The laboratory study known as a karyotype is represented by a photograph of a human’s chromosomes.
When cells are dividing, genes are arranged in two double pairs of chromosomes. Using high-resolution photographs, geneticists are able to analyze the photographs and then crop and arrange them in pairs to review a patient’s chromosome makeup.


Human chromosomes are made up of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which is a chain of nitrogenous bases – basic structures of DNA made up of Carbon (C), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) and Sulphur (S): CHONPS for its symbol on the periodic table – these bases are known as Thiamine, Cytokine, Guanine and Adenine – and give DNA its characteristic double helix shape.
The chromosome formula of all human beings is made up of 22 somatic (non-sexual) pairs, that is, 22 double copies – one from the father and one from the mother – and the sexual pair, where XX represents a woman and XY a man. Women always inherit an X, and men can inherit an X or a Y, so it is the sperm that determines the sex of the embryo.
In some cases, both the 22 somatic pairs and the sexual pair may have a formula different from the normal one, which may be:
- Deletions – loss of genetic material (chromosomal base pairs or DNA), which may be an entire chromosome (Monosomy) or only part of a chromosome.
- Duplications – gain of genetic material (chromosomal base pairs or DNA)
- Translocations - are structural arrangements of genes, different from the normal, where a chromosome fragment from one pair is exchanged with a chromosome fragment from another pair, and can be balanced or unbalanced.
- Inversions – in this case a fragment of the chromosome flips, that is, it changes its reading direction
- Monosomy – there is only one copy of the chromosome – either from the mother or the father
- Trisomy – there are 3 copies of a chromosome – in these cases there may be an inadequate division of the oocyte or sperm and they carry an additional copy of a chromosome
- Triploidy – in rare cases (only occurring in embryos or products of an abortion, as it is not compatible with life) we can find three copies of all chromosomes, which in almost 90% of cases is associated with hyper-fertilization (more than one sperm fertilizes an oocyte at the same time).
Endometrial receptivity test
The endometrial receptivity test is an advanced genetic study that allows us to determine whether the implantation window is at the right time in a woman’s cycle. The implantation window should be around 120 hours for an embryo on day 5 of development.

Your doctor can advise you if there is reason to believe the implantation window is not at the correct time.
This can lead to implantation failure, so your specialist will decide if this study is necessary.
The process involves taking an endometrial biopsy. After performing a replicable endometrial preparation, this biopsy is sent to a specialized genetics laboratory for processing. The laboratory typically provides the window in hours and performs additional microbiota tests—bacteria that live in the female tract that are positive and/or negative—and advises us on how to improve the environment or if the number of hours of the window needs to be modified.
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing
Noninvasive prenatal testing (NiPT) is a simple blood test that allows us to detect risk for chromosomal disorders.
During pregnancy, some cells move through the placenta into the mother’s blood, giving rise to something known as microchimerism. This generally occurs from the second week of pregnancy. In noninvasive prenatal testing, we take a blood sample from the mother or surrogate mother and analyze it for the baby’s cells. A genetic study with base sequencing is performed to detect chromosomal problems, such as partial or complete chromosome duplications and deletions.
These tests can also detect some microdeletions, as well as other genetic disorders, and also determine the baby’s sex and blood type for Rh incompatibility.

Paternity study
Paternity testing is performed to determine the genetic relationship with a baby during or after pregnancy.
Noninvasive prenatal paternity testing – by detecting microchimerisms in a maternal sample and comparing the sample with a cheek sample (taken with a swab scraping the patient’s cheek). The genetics of both partners – the baby and the potential father – are compared, and sequencing studies determine whether the similarities in the genome are sufficient to consider the father. This is done through gene comparison.
Postnatal paternity testing – by using a cheek sample from the newborn, child, or adult and a sample from the potential parent(s), a genetic comparison is made using nucleotide sequencing. This allows a determination of whether there are sufficient similarities in the genome to consider the father/mother.
In both tests, the result is given as a percentage of similarity and can more precisely indicate whether the relationship between the two can be determined without a doubt.


FDA kit
In the United States and Canada, regulations for accepting donated gametes are very strict and require donors to go through rigorous screening processes.
At Advanced Fertility Center Cancun, we not only have the necessary accreditations, certifications, and licenses to perform this type of process, but we are also one of the few clinics that can perform the tests required by the FDA for donor acceptance and process them through our FDA-approved laboratory partners. The tests, which consist of blood and urine samples—and may include other samples depending on the type of donation—are collected at the clinic and go through an initial processing process. The reports are submitted directly to our physicians for review and scheduling of international shipments.
Therefore, we can ship to almost all countries in the Americas and the rest of the world, with the certainty that the processes and studies we perform are endorsed by the highest international quality standards.